Sunday, April 17, 2011
Star Plots
A Star Plot is another graphic way of displaying multivariate information with each star representing a single observation and each spoke representing a variable.
Correlation matrix
A correlation matrix is represented by a number that depicts the relationship between two variables. The above matrices are an example of a correlation matrix among 20 climate model biases at certain spatial locations.
Similarity Matrix
Similarity matrices are used in aligning sequenced information such as higher scores are given more similar characteristics while lower scores are given dissimilar characteristics.Similarity matrices show a strong similarity to their counter matrices: distance and substitution. The above matrix is of the the Beatles song Hey Jude. The dark blue lined indicate similarity when lyrics are repeated. The area of unconcentrated shading is during the instrumental parts of the song.
Stem and Leaf Plot
A Stem and Leaf Plot is very similar to a histogram but demonstrates more information by way of summarizing the distribution of a data set while simultaneously providing data on individual values. All the data in a stem and leaf plot is arranged by place value from mean to median to mode. The larger digits are the stem and the smaller units are the leaves. Stem and Leaf plots are typically used when there are large amounts of data to be analyzed.
Box Plot
The Box Plot is a way of graphically identifying one or more sets of data. Box plots are best used when comparing distributions between several data sets.
Histogram
A Histogram is visual impression of the distribution of data shown by a graph. The above histogram is a simple example of a described problem: The number of weeks it takes to receive an order of contraceptives, and the frequency of the problem.
Parallel Coordinate Graph
A Parallel Coordinate Graph is a common way of visualizing and analyzing multivariate data. The above PCG visually communicates cancer statistics.
Trangular Plot
A Triangular Plot depicts the ratios of the three variables as positioned in a triangle. It is used in physical sciences to show the compositions of systems composed of three species, elements, resources, etc. The above triangular plot demonstrated the levels of flammability between three different gasses: Methane, Nitrogen, and Oxygen.
Windrose
Before the development of the compass rose, the windrose was a graphical display placed on maps to show the reader of the map a view of how wind speed blew and it's direction.
Climograph
A climograph is a depiction of the monthly precipitation and temperature in a selected place. In the above climograph, precipitation is shown by the bar graph while the line graph depicts temperature in Memphis, Tennessee.
Population Profile
A Population Profile is a chart dipicting a number of people as a function of their age. The above image shows the projected population structure with and without the AIDS epidemic in Botswana by 2020 from newborns to individuals in their eighties.
Scatter Plot
A Scatter Plot can demonstrate various correlations (or non correlations) between variables which can be positive, negative, or null. If the scatter plot begins from lower left to upper right, a positive correlation is suggested. Contrary, if the scatter plot begins from upper left to lower right, a negative correlation is suggested. Uncorrelated variables, such as displayed in the scatter plot above, show no correlation between variables- neither negative or positive.
Index Value Plot
Lorenz Curve
The Lorenz Curve demonstrates a proportion of distribution by graphing. The Lorenze curve typically shows probability using statistical information and is often used to analyze inequality between two numerical values. The Lorenz Curve shown above demonstrates the degree of inequality in the distribution of income.
Bilateral Graph
A bilateral graph demonstrates at least two variations of information . The above graph demonstrates the Augmented Trade-Weighted Index of the Australian dollar (shown in red) against the standard Trade Weighted Index from 1973-2008.
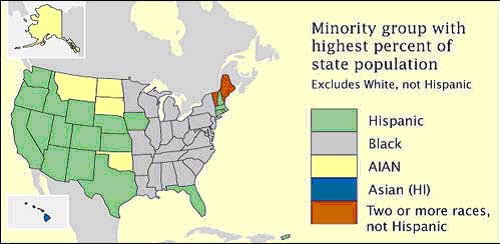
Nominal Area Choropleth Maps
Nominal Area Choropleth Maps define the measured area with predetermined variables such as states and borders or, in the case of the above image, minority groups and state population. Color schemes work well for displaying nominal data.
Unstandardized Choropleth Map
Unstandardized Choropleth Maps do not use numerous classes of variable totals but rather use only raw numbers. Using raw numbers instead of averaged numbers is good for more accurate analyzation of data. This map displays the total number of ski shops per county in Minnesota, Wisconsin, and Michigan.
Standardized Choropleth Maps
http://geoportal.icimod.org/TrainingandEducation/GISforBeginners/p1ch8/
A choropleth map becomes standardized when the variable values are determined using ratios, rates, percentages or proportions. The above image is of Access to safe drinking water in Nepal. The difference of intensity of color demonstrates the differences in phenomenon in rendered areas.
A choropleth map becomes standardized when the variable values are determined using ratios, rates, percentages or proportions. The above image is of Access to safe drinking water in Nepal. The difference of intensity of color demonstrates the differences in phenomenon in rendered areas.
Univariate Choropleth Maps
A Univariate Choropleth map is much the same as a bivariate choropleth with the exception that a univariate map displays only one set of data instead of two sets of unrelated data. The above image demonstrates the number of individuals living in poverty by county.
Wednesday, April 13, 2011
Bivariate Choropleth Maps
The purpose of a Bivariate Choropleth Map is to accurately demonstrate a relationship between different variables within the same map. To accomplish this task, bivariate maps require the use of distinctly different graphic symbols or colors. This particular map displays the percentage of people living in New York over 25 without a H.S. Diploma (Represented by blue circles) and the three colors represent percentages of population below poverty level.
Tuesday, April 12, 2011
Unclassed Choropleth Maps
An Unclassed Choropleth Map involves shading proportional data without actually classifying the data. With an unclassified choropleth map there can be as many intervals as there are areal units. The image on the left a classified choropleth map using interval classification. The image on the right is an unclassified choropleth map of the same image.
Sunday, April 10, 2011
Classed Choropleth Maps
A thematic maps is a map which portrays a specific theme with a geographical location. The Classed Choropleth Map is a map used as a visual aid to show measurement, by proportion, by using color shading or patterns.
Range Graded Proportional Circle Map
Continuously Variable Proportional Circle Map
A Continuously Variable Proportional Circle Map links the size of it's circles to the density data in a population within an area.
DOQQ
Digital Orthophoto Quarter Quads are aerial photographs produced by the United States Geological Survey.
Currently, Color infrared and black & white DOQQ projections are available.
Currently, Color infrared and black & white DOQQ projections are available.
DEM
The Digital Elevation Model is a grid representing elevated points on the earth's land surfaces.
Saturday, April 9, 2011
DLG
www.mass.gov/mgis/trnslns.htm
A Digital Line Graph represents cartographic information and are usually derived from USGS maps. DLG's are distributed in three scales: Large, intermediate, and small.
A Digital Line Graph represents cartographic information and are usually derived from USGS maps. DLG's are distributed in three scales: Large, intermediate, and small.
LIDAR
LIDAR or Light Detection and Ranging is an optical remote sensing technology that illuminates the target by means of ultraviolet, near-infrared, or visible light. This illumination through LIDAR helps measure the distance and other properties of a target.
Doppler Radar
A Doppler Radar measures the speed at which signals are returned from an object at a distance. The signal is sent to the object from the Doppler and then the frequency of the returned signal is analyzed to determine the object's motion. Doppler radar is used in meteorology, aviation, radiology, and in police forces.
Black and White Aerial Photography
Aerial Photography are images captured via satellite or by high flying aircraft. As we know, light and energy are emitted from the sun. The types of light emitted are divided into visible and invisible spectrums. The invisible near-infrared wavelengths of light are captured by electronic sensors or film designed to pick-up these wavelengths. From the early 20th century to present day black and white aerial photography has been used. It was much more widely used up until the second world war however. When color infrared film hit the market, less aerial photographs were taken using black and white infrared film.
Infrared Aerial Photo
Infrared Aerial Photography are images captured via satellite or by high flying aircraft. As we know, light and energy are emitted from the sun. The types of light emitted are divided into visible and invisible spectrums. The invisible near-infrared wavelengths of light are captured by electronic sensors or film designed to pick-up these wavelengths. When near-infrared images are combined with visible wavelengths, the combination provides a unique way of viewing vegetation health, land formations, pollution, and other happenings on the earth's surface.
Thursday, April 7, 2011
Cartographic Animations
http://cartography2.org/Chapters/page6/OverviewAnimated.html
Cartographic Animation is a visualization tool used to help demonstrate change. This change is categorized into two different ways:
Temporal: Change over periods of time
Non-Temporal: Variables in a single time period.
Most cartographic animations depict change temporally- Over time.
Cartographic Animation is a visualization tool used to help demonstrate change. This change is categorized into two different ways:
Temporal: Change over periods of time
Non-Temporal: Variables in a single time period.
Most cartographic animations depict change temporally- Over time.
Statistical Maps
prolifescranton.org/Maps.php
The Statistical Map (aka the distribution map) uses graphics do display information pertaining to a specific subject. The graphics typically represent how often something takes place in a geographical location. The statistical map above demonstrates the difference in statutes pertaining to the amount of parent involvement required for an abortion in each state.
The Statistical Map (aka the distribution map) uses graphics do display information pertaining to a specific subject. The graphics typically represent how often something takes place in a geographical location. The statistical map above demonstrates the difference in statutes pertaining to the amount of parent involvement required for an abortion in each state.
Wednesday, April 6, 2011
Cartograms
www.asianoffbeat.com/default.asp?Display=1052
A Cartogram Map re-sizes a given territory depending upon the variable being mapped such as land area or population. Cartograms are great for mapping one desired variable and nothing else. The map on the top reflects the amount of deaths in 2002 from preventable diseases while the map on the bottom reflects the countries size relative to its population.
A Cartogram Map re-sizes a given territory depending upon the variable being mapped such as land area or population. Cartograms are great for mapping one desired variable and nothing else. The map on the top reflects the amount of deaths in 2002 from preventable diseases while the map on the bottom reflects the countries size relative to its population.
Flow Map
Isopleths
http://www.newmediastudio.org/DataDiscovery/Hurr_ED_Center/Hurr_Structure_Energetics/Closed_Isobars/Closed_Isobars.html
An Isopleth is essentially an Isoline. Lines or contours connect natural occurences in equal amounts in any given area. these contours portray a 3rd dimention on a map.
An Isopleth is essentially an Isoline. Lines or contours connect natural occurences in equal amounts in any given area. these contours portray a 3rd dimention on a map.
Isohyets
Tuesday, April 5, 2011
Isotachs
http://start.tamu.edu/2008/200804/20080423/00Z_nam_all_24h.html
Isotachs (together with Isolines) connect points of equal wind speeds on a natural surface.
Isotachs (together with Isolines) connect points of equal wind speeds on a natural surface.
Isobars
An Isobar Map shows a 3-dimentional view of equal atmospheric pressure on a meteorological map. Isobars do not touch or cross.
Isoline maps
http://legacy.sfei.org/ecoatlas/GIS/MapInterpretation/MapsandScales.html
Isoline Maps show patterns that when displayed on a 2-dimensional map display a 3-dimensional (usually overhead view) of environmental surfaces. Dimension in the map above was accomplished by connecting points of equal value (Isolines) to give the reader a better understanding of where elemental change takes place. This interpolation differentiates higher value from lower value and measures several elements of the natural environment such as elevation, wind speed, and rainfall to name a few.
Proportional Circle Maps
http://www.geog.ucsb.edu/~jeff/gis/proportional_symbols.html
A Proportional Circle Map uses circles to represent a total data value within a geographical area on a map. Circles are used over other shapes because statistical information can be more accurately scaled to size on a map using the radius of a circle to represent an area. The bigger the circle, the bigger the geographical location the circle represents. To the human eye, circle proportion is an easy way to understand and differentiate scaled values on a map.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)